
In a world where every piece is shared on social media, people tend to change their lifestyles in accordance with the modern trend. They look for content in everything and everyone around them. This habit has proved to be fruitful in certain aspects. They happen to be very concerned about their food habits and their body image. This has led to so many practices that are aimed to help people with these concerns. Coming to the question in hand, is the gluten-free diet going to help a person? Like every other thing around, this has its boons and banes as well.
What is gluten? They are a family of proteins, called prolamins and glutelins found in wheat, barley, rye, and spelled. The name comes from the Latin word ‘Glue’ as it gives a sticky consistency when mixed with water which makes it ideal to be used for the bakeries. Many people feel uncomfortable after the consumption of foods that contain gluten. The most severe condition after gluten consumption is the ‘celiac disease’.
Gluten-free making miracles in weight loss!
A gluten-free diet eliminates all foods containing gluten. Gluten is the main ingredient present in almost all the foods available in the market like wheat, rye, cross-contaminated oats, in sauces like soy sauce, malt, vinegar, flour and as additives or fillers. Foods to avoid in a gluten-free diet are- wheat, barley, rye, malt, brewer’s yeast. Food to include- meats and fish, eggs, dairy, fruits and vegetables, grains, nuts and seeds, spreads and oils, beverages, herbs and spices.
- When going gluten-free the most noticeable changes are having to relinquish favorite staples of bread, pasta, cereals, and processed snack foods. All these products are highly processed and contain high calories and lack other nutrients [1] going gluten-free thus reduces the consumption of all these unhealthy foods, as said by Dr. Maithili Paranjpe(nutritionist).
- All the celebrities for weight loss and athletes for improved performance started switching to a gluten-free diet. The global market for gluten-free products grew at an annual rate of 28% [2]. A 2013 study found that 65% of adults think gluten-free foods are healthier and 27% choose gluten-free products to aid in weight loss [3].
- A gluten-free diet leads to more consumption of fruits and vegetables which contain a good amount of fiber and antioxidants which help in weight loss.
- Studies have shown that the elimination of gluten from the diet also helps in treating GI disturbances [4].
- According to Dr. Maithili Paranjpe, gluten begins in an inflammatory response which can lead to weight gain.
- A gluten-free diet helps boost energy levels and helps one from feeling tired and sluggish [5].
- The gluten-free diet has helped patients have rapid improvement of symptoms like diarrhea, steatorrhea and weight loss [8].
- A study carried out from the year 2009 to 2014 showed that a gluten-free diet was associated with a decrease in weight over 1-year, lower waist circumference and higher high density of lipoprotein levels compared to the general population [12].
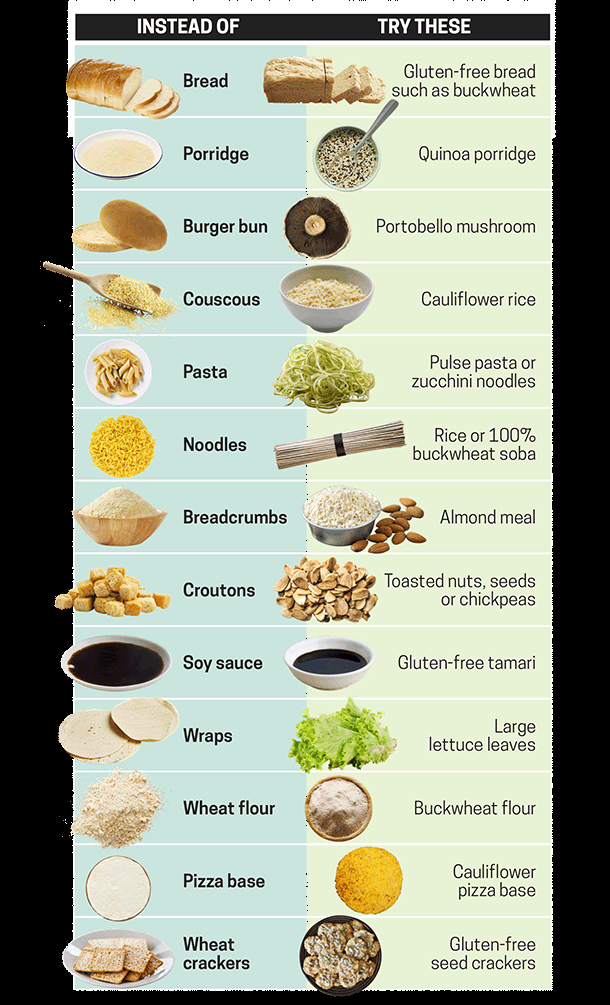
Think wisely before adopting gluten-free as a lifestyle.
The avoidance of gluten as suggested by the health professional (Ashish Sarkar) should be in the patients with celiac disease or those with gluten intolerance. But over the period of time, the avoidance of gluten has extended to the healthy population [11]. Despite having a variety of health benefits, a gluten-free diet can have some downsides. Some of the major problems that concern health professionals when we talk about a gluten-free diet are-
- Risk of Nutritional deficiencies
- People who follow a gluten-free diet for a very long period of time are at the risk of several nutritional deficiencies. These include deficiency in fiber, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, folate, zinc, vitamin A, D, E and K and more [6]. Studies have also shown that a gluten-free diet does not help to treat any deficiencies and these deficiencies occur because people choose processed food labeled as gluten-free rather than opting for fruits and vegetables [7].
- Constipation
- It is one of the common side-effects of a gluten-free diet. This happens because gluten-free eliminates may foods like bread and bran which are a good source of fiber. Consumption of fiber-rich foods has been proven to improve bowel movement [8].
- Many gluten-free substitutes of the diet are low in fiber and thus can be one of the reasons for constipation [9].
- Cost
- Studies have been carried out to check the difference in the cost of gluten-free products in comparison to its regular counterparts and it has been proved that it costs two and half times more than our normal diet [10]. This can be because the gluten-free products have costlier raw material and then have to go through many tests also, many safety measures need to be carried out to avoid contamination.
Along with gluten-free being a difficult lifestyle to be followed, studies are showing that it can lead to weight gain. In a study of 369 adults with celiac disease who follow a gluten-free diet for an average of about2.8 years, 22 of 81 (27%) initially overweight or obese patients gained weight. In another study, 82% of people were reported to gain weight after following a gluten-free diet for about 2 years. Among children, the percentage of overweight children almost doubled after following a gluten-free lifestyle for over a year [13].
Take away-
Each individual is different and even the body requirements are different, we need to listen to our body and choose a lifestyle that suits us. Social media as believed is both a boon and a curse. Following diets just by reading about it on media or because of some celebrity endorsement can often lead to life-threatening conditions. Diets like a gluten-free diet can be beneficial for one and harmful to other. Always refer to authentic researches and take professional advice preferable from a nutritionist before following any kind of diet.
References
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-weight/diet-reviews/gluten-free-diet-weight-loss/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5439366/
- https://www.foodnavigator-usa.com/Article/2013/10/15/Healthy-eaters-dieters-not-celiacs-propelling-gluten-free-market
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/79/4/669/4690166
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3482575/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17472877-nutritional-deficiencies-in-celiac-disease/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257612/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15051613-effect-of-a-gluten-free-diet-on-gastrointestinal-symptoms-in-celiac-disease/
- https://jandonline.org/article/S0002-8223(00)00386-2/fulltext
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18783640-gluten-free-and-regular-foods-a-cost-comparison/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5866307/
- https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Dig+Dis+Sci.&title=Obesity,+metabolic+syndrome,+and+cardiovascular+risk+in+gluten-free+followers+without+celiac+disease+in+the+United+States:+results+from+the+National+Health+and+Nutrition+Examination+Survey+2009-2014&author=H-S+Kim&author=MF+Demyen&author=J+Mathew&author=N+Kothari&author=M+Feurdean&volume=62&issue=9&publication_year=2017&pages=2440-2448&pmid=28451915&
- https://jandonline.org/article/S2212-26721200743-5/fulltext